Review Article
1 Centre for Human Reproduction, India.
2 Ex-Rotunda-A Centre for Human Reproduction.
3 Consultant Neurologist Swami Satyanand Hospita.
*Corresponding Author: Kulvinder Kochar Kaur
Citation: Dr Kulvinder Kochar Kaur, DR Gautam Nand K Allahbadia, DR Mandeep Singh. The importance of Dysbiosis in Intestinal flora Subsequent to ischaemic Stroke: Implications in Therapeutic Management and Biomarkers for Prognosis-A Narrative Review, J. Clinical and Medical Research and Studies. 2(1)
Copyright: © 2023 Dr Kulvinder Kochar Kaur, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons
Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: January 20, 2023 | Accepted: January 27, 2023 | Published: January 30, 2023
Abstract
Stroke represents an acute cerebrovascular disease that can result in unanticipated burst of cerebral vessels or secondary to vascular blockade;further known as haemorragic Stroke(HS) or ischaemic Stroke(IS) respectively.The incidence of IS is considerably greater in contrast to HS which is implicated in about 80% of the full incidence of cerebrovascular damage.The disrupted blood provision to brain regions is associated with hypoxia,further results in IS correlated nerve cerebral injury. Numerous risk factors were implicated in the causation of or ischaemic Stroke that resulted in considerably greater burden regarding the patient’s family along with that for the society in general
Keywords: ischaemic Stroke(IS) ; brain gut axis; dysbiosis ; Intestinal flora ;SCFA’s ischaemic stroke(IS) ; brain gut axis; dysbiosis ; intestinal flora ;SCFA’s
Introduction
Stroke represents an acute cerebrovascular disease that can result in unanticipated burst of cerebral vessels or secondary to vascular blockade;further known as haemorragic Stroke(HS) or ischaemic Stroke(IS) respectively[1].The incidence of IS is considerably greater in contrast to HS which is implicated in about 80% of the full incidence of cerebrovascular damage.The disrupted blood provision to brain regions is associated with hypoxia,further results in IS correlated nerve cerebral injury. Numerous risk factors were implicated in the causation of or ischaemic Stroke that resulted in considerably greater burden regarding the patient’s family along with that for the society in general [2]. Of the risk factors the ones of maximum significance are hypertension, Diabetes as well as atherosclerosis. ischaemic Stroke further is a complicated disease that takes place secondary to variable environmental along with genetic factors. Numerous local along with International studies illustrated that 2 kinds of risk factors are there regarding IS like i)non modifiable[3] (like gender ,age, genetic factors,family history,race) along with those that are modifiable(hypertension aberrant blood glucose, hyperlipidemia ,Atrial Fibrillation,greater homocysteine quantities,poor living conditions).For avoidance of risk factors they need to be tackled in particular the most inimical ones , like hypertension as wellas Diabetes for reduction of the incidence along with mortality of this disease.
Intestinal flora is inclusive of all the microorganismspresent in the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT), constitutedof amongst 150,000-36,000 bacterial species(spp)mostly made up of Firmicutes along with Bacteroides phyla [5]. Furthermore, an ecosystem comprised of trillions of commensals in the form of bacteria, archaea, protozoaas well as viruses along with bacteriophages whose collective microbiome is known as microbiotaor comprise the Intestinal flora [6]. Intestinal flora possess the capacity of controlling the metabolic activity along with controlling the Intestinal immune system as well as biological barriers [7], hence possess a part in the sustenance of health of the host [8]. The total quantities of bacteria along with species(spp’) that constitute the Intestinal flora might be influenced by various factors like environment [9], diet [10], utilization of medicines along with genetics. Intestinal microbiome comprises of Intestinal flora with its surrounding Intestinal milieu,that works for the sustenance of the homeostasis of the internal milieu in case of normal situations for humans as well as animals .On loss of homeostasis of the this internal micro-ecosystem different diseases are generated,that might implicate the central nervous system(CNS[11].The Intestinal microenvironment alterations results from alterations in the Intestinal micro-ecosystem, influence the Intestinal function regarding absorption along with metabolism,thus followed by IS[12], maximum directly or indirectly. Additionally, the enteric nervous system (ENS)alias the second ‘’human brain’’ possesses the capacity of crosstalking with the CNS, autonomic nervous system (ANS) [13], hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (H-P-A) axis along with other structures to for generating a two-way controlling axis alias the brain-gut axis. Furthermore, intestinal flora has the capacity ofdecomposing the food particles that have been fermented to generate variable metabolites [14], which possess a significant part in the brain-gut axis. It might produce a network of nerve, immune along with endocrine controlling by stimulating neuroendocrine along with conduction pathways that represents the ‘’flora- gut -brain- axis’’. Alterations in intestinal flora can alter the intestinaldefense brain function along with intestinal permeability [15], that influence the ENS along with CNS.
Simultaneously intestinal flora have a significant part in the generation of the CNS [16, rev by us in17,18]. Different studies have illustrated that gut microbiota possess the capacity of controlling neurotrophic factors or proteins implicated in brain generation along with plasticity like the brain derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF) [19], synaptophysin as well as post synaptic dense region proteins.The sterile status of sterileanimals can result in alterations in the nervous system like escalated permeability of the blood brain barrier(BBB). Microglial cells are variable from canonical bacterial colonizationanimals in morphology along with function [20]. Additionally, intestinal flora is further implicated in CNS actions like anxiety, depression along with stress reactions [21]. Having reviewed earlier the role of Gut Microbiota inavoidance of obesity, Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), associated with generation of neurodegenerative along with neuropsychiatric diseases [22-27]. Here we reviewed how imbalanced intestinal flora presence there can be enhanced risk of stroke via various mode. Normally intestinal flora that continue to be in steady state has a considerably significant part in sustenance of normal brain function along with healing. On imbalanced intestinal flora presence there can be enhanced risk of stroke via various modes.
Methods
Here we conducted a narrative review utilizing search engine pubmed,google scholar ;web of science ;embase; Cochrane review library utilizing the MeSH terms like ischaemic Stroke(IS); Intestinal flora; ’flora- gut -brain- axis’’; BDNF; BBB; atherosclerotic plaque; Porphyromonas gingivalis; short chain fatty acids (SCFA); toll like receptors ( TLRs); trimethylamine-N-oxide(TMAO); phenylacetic acid glutamine (PAGln); Intestinal junctional proteins; Intestinal permeability Lactobacillus rhamnosus from 1975 till 2022 till date.
2.Intestinal flora along with their products result in stroke by atherosclerosis Induction
Activation of platelets, their adherence along with atherosclerotic plaque production represent significant factors regarding pathogenesis of IS(Figure1)[rev in 28].
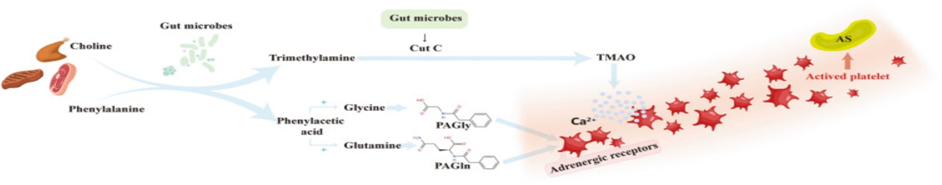
Legend for Figure 1
Courtesy ref no- 28 -Some intestinal metabolites promote the development of atherosclerosis. Choline in food is transformed into trimethylamine by the action of intestinal bacteria, and the latter is formed into TMAO by the action of a specific group of bacteria containing the CutC gene. TMAO evokes the release of intracellular calcium stores and promotes platelet activation and atherosclerotic plaque formation. Phenylalanine in food is converted to phenylacetic acid by the action of porA gene-containing enteric flora, which synthesizes PAGln or PAGly with glutamine or glycine and binds to platelet adrenergic receptors to induce platelet hyperreactivity and promote atherogenic plaque formation
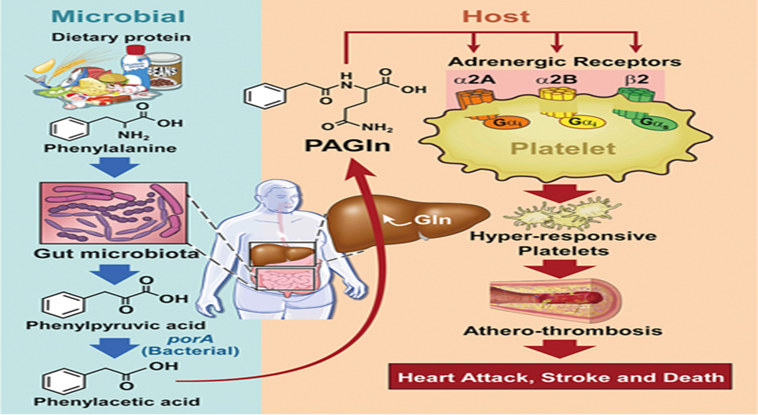
More recently studies have illustrated that intestinal flora a significant part in the atherosclerotic plaque generation. There are3 modes by which intestinal flora possess participate in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques; namely i) Activation of the immune system by the bacterial infections [29],by impacting different immune cells [30]. Furthermore, the expression of toll like receptors ( TLRs) by macrophages result in escalated proinflammatory cytokines as well as chemokines , that aggravates the propagation of atherosclerotic plaques along with result in the generation of a susceptible plaque generation.For facilitation of atherosclerosis,the microbes implicated are Porphyromonas gingivalis[31],Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Chlamydia Pneumoniae[32], along with othersii)Food metabolism by intestinal flora like of cholesterol as well as fat influence the generation of atherosclerotic plaques[33]. Proinflammatory microorganisms transplantation possess the capacity of reduction of kinds of microorganisms,that generate short chain fatty acids (SCFA)in mice,escalate the inflammatory reaction along with facilitate atherosclerosis generation[34].Some types of bacteria like Lactobacillus rhamnosus (LGG)or certain pharmacological substances like telmisartan(TLM) supplementation possess the capacity of changing bacterial genera along with reduction of α-diversity , possessing significant association with atherosclerotic plaque size,plasma -A- fatty acids binding protein (FABP) along with cholesterol quantities[35].iii)Some metabolites like, trimethylamine-N-oxide(TMAO), generated by intestinal flora facilitate atherosclerotic plaque generation by activating platelets activities.The TMAO pathway is believed to be the pathway being maximum direct one ,where intestinal flora impact the event of atherosclerosis[36].
Choline from the diet undergoes metabolism by intestinal flora to form trimethylamine,that gets oxidized to TMAO, subsequent to gaining entry in liver through liver-gut circulation. TMAOfacilitates the liberation of intracellular Ca2+ ions in an extracellular manner that is in a platelets activator fashion,hence modulates the greater platelets reactivity along with escalates the risk of thrombosis generation[37].
Besides animal experiments , clinical studies have further illustrated the implications of TMAO in atherosclerosis generation, that is significantly associated with the risk of cerebrovascular along with cardiovascular processes.A study performed by Tang etal.[38], implicating 4007 individuals, followed up for3yrs for assessment of correlation amongst the quantities of plasma TMAO along with the risk of cerebrovascular along with cardiovascular processes.Their outcomes obtained illustrated a positive association with the risk of thrombosis in a dose based fashion,an action independent of canonical cardiovascular disease (CVD) along with cerebrovascular disease risk factors. However, Yin etal.[39], in their study did not observe escalated plasma TMAO quantities in case of stroke patients or patients presenting with transient ischaemic attack (TIA). They further evaluated the variations in the intestinal flora components along with TMAO quantities in asymptomatic patients with atherosclerosis, stroke or TIA. Their outcomes obtained demonstrated that the TMAO quantities along with intestinal flora constituents were akin in asymptomatic patients with atherosclerosis,with or without carotid plaques. Nevertheless, intestinal flora composition in stroke or TIA patients was considerably significantly variable from those of asymptomatic atherosclerosis patients. Noticeably,despite the TMAO quantities were not escalated as anticipated ,the quantities were still lesser in contrast to those seen in asymptomatic atherosclerosis patients. Tang etal.[38], reasoned that the utilization of medicines for stroke treatment might decrease the TMAO quantities.Hence the association amongst the intestinal flora product TMAO as well as stroke requires further assessment to prove this posit.It was observed that the microbial cut C gene was implicated in, trimethylamine(TMA) transformation along with escalated the size of infarction,thus this gene can be believed to facilitate dysfunctional neurological function by genetic engineering bacterial transplants by modifications in germ free(GF) mice,pointing that GM possess the capacity of exaggerating infarcts by generating TMAO[40]. Other than TMAO,other metabolites of intestinal flora possessing the capacity of platelet activation inclusive of phenylacetic acid glutamine (PAGln) along with phenylacetic acid glycine (PAGly)[41].These reflect phenylacetic acid whose consumption occurs in diet followed by transformation to phenyl alanine by intestinal flora along with finally into glutamine as well as glycine respectively. PAGln along with PAGly are akin in structure to adrenergic receptors,hence possess the capacity of binding to plateletβ2 receptors in the body along with capacity of platelet activation for facilitating thrombosis. Nevertheless, certain studies observed that PAGly possesses the capacity of activating Gαi/PI3K/AKT signaling cascade via stimulation of β2AR, thus cell apoptosis in addition to reduction of the region of myocardial infarction (MI) that occurred due to ischaemia /reperfusion (I/R) damage. Nevertheless, therapy with greater dosage would result in greate rmortality rate [42]. It can be seen that the part of PAGly in body is intricately correlated with its dosage. Nevertheless, the part of PAGly subsequent to IS along with the modes by which it works have not been clarified till now, thus needs greater assessment (Figure1).
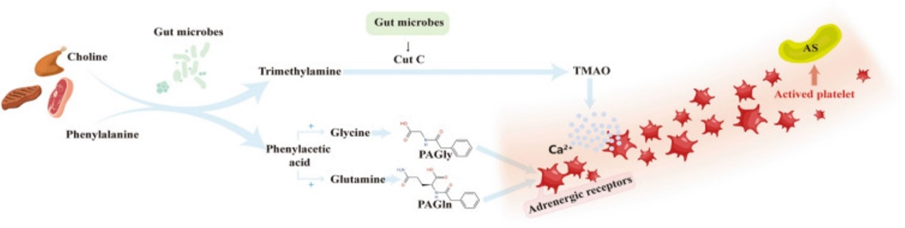
Legend for Figure 1
Courtesy ref no- 28 -Some intestinal metabolites promote the development of atherosclerosis. Choline in food is transformed into trimethylamine by the action of intestinal bacteria, and the latter is formed into TMAO by the action of a specific group of bacteria containing the CutC gene. TMAO evokes the release of intracellular calcium stores and promotes platelet activation and atherosclerotic plaque formation. Phenylalanine in food is converted to phenylacetic acid by the action of porA gene-containing enteric flora, which synthesizes PAGln or PAGly with glutamine or glycine and binds to platelet adrenergic receptors to induce platelet hyperreactivity and promote atherogenic plaque formation Porphyromonas gingivalis,that resides in oral cavity was also observed to be correlated with stroke generation further has to be borne in mind[43].
3.Alterations in intestinal flora can influence brain healing subsequent to stroke
The ‘’flora- intestine- brain’’ area is a newer abstraction.It has beena prior needed posit,that illustrated in the model of middle cerebral artery occlusion(MCAO), intestinal flora possessed a considerably important influence on stroke prognosis.Benakis etal.[44],revealed that secondary to antibiotics,dysbiosis possessed the capacity of reduction of α-diversity of intestinal flora along with escalate the prognosis;the histology demonstrated a reduction of volume of the ischaemic tissue.This action takes place secondary to the reduction of IL-17+γδ T cells along with the escalation of Treg cells in the small intestine,thus restricted the infiltration of inimical substances into the brain membrane of IL-17+γδ T cells.Sun et al.[45], observed that the butyric acid bacteria possessed the capacity of reduction of cerebral I/R damage in diabetic mice by controlling intestinal flora 16S RNA gene sequencing in combination with liquid chromatography(LC)-MS(high resolution mass spectrometry ) assessment illustrated that incase of rats with IS there were alterations of intestinal flora along with plasma metabolites. Furthermore,it was demonstrated that the enrichment of Proteobacteria, Firmicutes in addition to Defferibacteres was significantly variable amongst Sham along with IS groups.A robust association amongst the gut microbiota(GM) with the dyscontrolled metabolites was present[46].Xu etal.[47], observed that the MCAO mice expanded the dynamic dysbiosis at fast pace .The escalated Enterobacteriaceae bacteria accelerates cerebral infarction by escalating systemic inflammation. Akin studies illustrated that dyscontrolled microbiotais partly implicated in poor prognosis of patients presenting with primary stroke.The utilization of aminoguanidine or superoxide dismutase(SOD) for reduction of nitrate generation or by utilizing tungstate for hampering nitrate respiration possesses the capacity of hampering Enterobacteriaceae bacteria overgrowth,decrease systemic inflammation along with reduction of risk of cerebral infarction.These therapeutic actions are based on the GM, that pointed to the translational importance of gut- brain axis regarding the treatment of stroke.Wang etal.[48],validated that in the patients of T2D subsequent to AIS the serum quantities of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) as well as D-lactate enhanced in a clear manner. Additionally, she demonstrated that the butyrate generating bacteria inclusive of Lachnospira, Blautia along with Butyricoccus reduced. On replenishment of BS,the mice demonstrated lesser quantities of proinflammatory cytokines besides illustrating smaller volume of infarction. Furthermore,it illustrated that fecal transplantation possessed the capacity of ameliorating ischaemic stroke damage by conferring protection to the BBB.One day subsequent to stroke MCAO models of pigs [49], demonstrated a reduction in microbial diversity as well as on day3 there existed a negative association of the volume of the injured area with microbial diversity.In correlation with the models the enrichment of Proteobacteria was significantly escalated, whereas reduction of Firmicutes,other lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus took place on day3 post stroke .These outcomes from a pig model point to the plasticity of gut microbiome at the time of acute phase of stroke besides impacting the injury.
3.2 Alterations in intestinal mucosal permeability can impact stroke results
Intestinal mucosal barrier which is unbroken represents a significant defense for the body for avoidance of inimical external factors. At the time of IS alteration of intestinal permeability takes place secondary to different explainations, usually presenting in the form of escalated intestinal permeability. This causes enhanced toxic products entering blood circulation via the intestinal mucosal, followed by entry into the nervous system resulting in injury. The dysfunctional Intestinal barrier function in patients with cerebral infarction might be associated with these factors detailed hereafter.
3.2AIschaemic Stroke results in the reduction of expression of Intestinal junctional proteins
The Intestinal mucosa inclusive of the structure of tight junctions (TJ) are comprised of numerous proteins subunits [50], of whom claudins as well as occludins are of considerable importance in view of their crucial structural part. Numerous studies [51], have evaluated their expressional quantities in the form of changed mucosal permeability. A reduction in the expression of zonula occludens 1(ZO1), occludins along with claudins takes place subsequent to stroke[52]. Cerebral infarction reduces the expression of Intestinal mucosa tight junction proteins. Occludin which results in the breakdown of tight junctions, injures the Intestinal barrier as well as enhances intestinal permeability. Xia etal.[53], observed that the expression of ZO1, VE-cadherin, occludins along with claudin 5 in case of rats of MCAO group were apparently decreased in variable extents. Delivery of Shengui Shansheng Pulvis(SSP) resulted in restoration of these proteins in the intestinal mucosal epithelium with simultaneous reduction of MCAO induction of brain oedema along with enhanced the expression of VIPR1/2 in the OGD BBB models decreasing endothelial damage.
3.2BEnhanced Intestinal epithelium permeability stimulated by micro-RNA subsequent to stroke
microRNA represents a type of small noncoding ribonucleic acid which take part in different pathophysiological events of the body.miR-21-5p represents a type of mi RNAs.Wu etal.[54], observed that there was significantly enhanced miR-21-5p in serum of patients with cerebral infarction. In different studies it has been observed that miR-21-5p possesses the capacity of escalating intestinal epithelium permeability by causing upregulation of small GTPase-ADP- ribosylation factor 4(ARF4) [55].The capacity of miR-21-5p to escalate vascular permeability has been illustrated in akin studies of colorectal cancer along with that might be correlated to its targeting of Krev interaction protein1 along with activation of the β-catenin signaling pathway .Impairment of intestinal flora subsequent to stroke, generates toxic metaboliies working on the intestinal mucosal epithelium .
LPS along withK99 pili protein localized in the brain 24h subsequent to stroke was observed by Kurita etal.[56], that was present in the Iba-1 positive neurons, microglia along with endothelial cells.These outcomes obtained pointed that ischaemia Induction of Enterobacteriaceae proliferation resulted in escalated luminal LPS quantities, caused weakening of the tight junctions of the epithelial cells along with facilitated the entry of LPS in the circulatory system. Singh etal.[57], observed that the intestinal flora could be impacted subsequent to stroke.Once intestinal flora imbalanced,opportunistic pathogens can generate ion different inimical substances,like LPS. LPS comprises of the cell wall constituentof gram negative bacteria alias endotoxin,that possesses the capacity of impacting tight junctions of the intestinal epithelium along with result in escalated intestinal permeabilityby modulating the TLR4/MyD88, signal transduction pathway. Escalation of TLR4 positive cells got initiated 1h subsequent to MCAO,persisting for22 h.In particular knockout of TLR4had the capacity to generate a protective action against Ischaemic stroke .Thus it is clear that TLR4 is an important target in case of stroke[58]. Interference of GM could result in cerebral endothelial cells via the endothelial nitric oxide synthase(eNOS) reduction of activity [59]. Stroke can result in escalated enrichment of gram negative Enterobacteriaceae bacteria along with further escalate circulatory LPS quantities [56,60], that might initiate inflammation through TLR4[61] along with change intestinal mucosal ligand protein expression quantities causing a leaky gut.In the meantime LPS causes induction of an inflammatory reaction that further aggravates stroke damage . This pointed that stroke along with changed intestinal flora are biphasic. Furthermore, cerebral artery lysates of antibiotics treated rats the eNOS-P/total eNOS ratio was reduced in contrast to controls. Utilization of antibiotics causes the interference of GM leading to cerebral endothelial impairment. Nevertheless, this study was converse of that by Benakis etal.[44]. The intestinal barrier is the main defense against the external environment that possesses a significant part in guaranteeing the stability of internal milieu of the body. Blood DAO (diamine oxidase), D-Lac(D-lactate) along with endotoxins [64], are dependable pointers that towards the function of intestinal barrier.Mice having hyperuricemia were observed to have injured intestinal barrier along with escalated Intestinal permeability. that result in an induced inflammatory event. Escalated serum uric acid quantities were observed to be correlated with an escalated risk of Ischaemic Stroke,however the mode is not clear. Actually, Joshua etal.[63], observed akin outcomes in animal studies. Nevertheless, various studies [64], concluded that not enough validation for alterations in the morphology along with expression of permeability proteins in the intestinal mucosal epithelium subsequent to MCAO (Fig2).
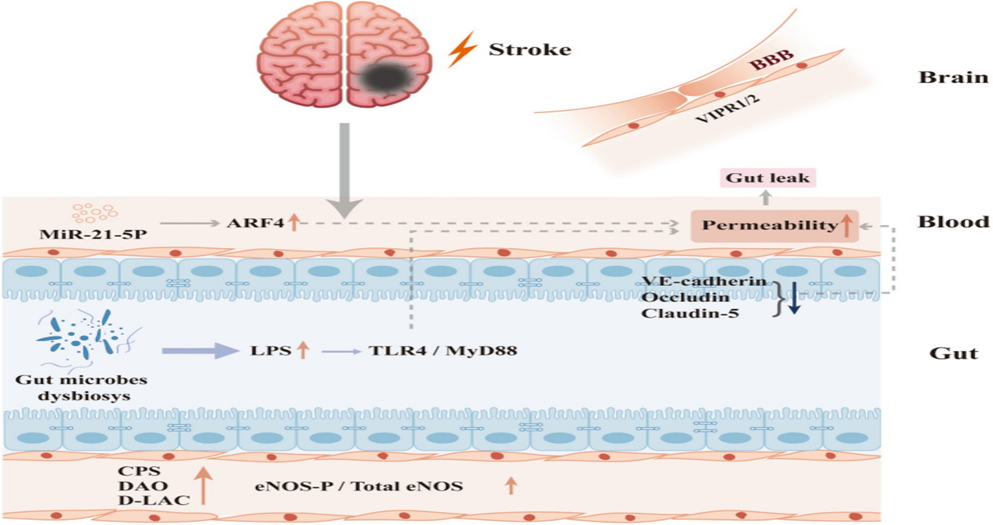
Legend for Figure. 2
Courtesy ref no- 28 -Post-stroke intestinal changes and their impacts on cerebral organization. Stroke causes a reduction in the expression of intestinal epithelial tight junction proteins including VE-cadherin, Occludin and Claudin-5; more LPS is produced by post-stroke intestinal flora, which induces damage by binding to TLR4/MyD88 in the downstream inflammatory response; LPS also contributes to an increase in eNOS-P/total eNOS, causing vascular endothelial damage; stroke causes an increase in miR-21-5p and further upregulated ARF4; the aforementioned factors combined lead to increased intestinal mucosal permeability and leaky gut. The blood LPS, DAO and D-LAC elevated after vascular endothelial injury and BBB endothelial injury accompanied by VIPR1/2 decreasing
4.Cytokines liberated by gliacytes along with other Cell kinds Post Ischaemic Stroke might either
Ischaemia along with hyoxia in brain tissue from different etiologies stimulate a series of stepwise reactions inclusive of glial cell activation along with liberation of proinflammatory mediators, resulting in activation of endothelial cells that express adhesion molecule along with enrol inflammatory in addition to immune cells from circulation at the region of stroke damage.The concomitant liberation of damage–associated molecular pattern receptor (DAMP)/ cytokines besides the activation of the vagal nerves causes disordered intestinal motility,other intestinal aberrations in addition to escalated intestinal permeability.Vila etal.[65], observed that serum quantities of Tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNFα) as well as interleukin-6( IL-6) during admission possessed a robust correlation with early neurological inimical effects . Nevertheless, the precise source of IL-6 along with TNFα were not revealed in the study. Numerous studies [66] illustrated that the time period subsequent to a stroke could cause escalated expression of proinflammatory/inflammatory factors in the serum along with in the brain tissue.This aggravated local or systemic inflammatory reaction along with further exacerbates the brain tissue injury. Primary culture astrocytes were observed to be expressing minimal quantities of TLR2, TLR4, TLR5 along with TLR9 at the time of resting culture situations,however their mRNA expression quantities were remarkably upregulated on exposure of cells to particular bacteria obtained ligands[67]. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 (TREM1) gets generated by Ly6C+ MHCII+ macrophages that are present in lamina propriaof the intestinal mucosa subsequent toa stroke;its capacity of escalating mucosal epithelial permeability facilitates bacterial translocation across the intestinal barrier into the brain tissue[68].This has relevance regardingthe peripheral TREM1 results in escalated proinflammatory reaction to brain obtained as well as gut obtained immunogenic constituents. Hampering TREM1 has the capacity of decreasing brain injury via this particular innate immune pathway.Earlier activation of PMN in the ischaemic braintissue might be secondaryto fast liberation of DAMPs along with ultimately result in the liberation of IL-1b[69].This is an event that facilitates the initiation of vesicle generation by activation of immune cell surface receptors besides the activation of the NLRP3 pathway.On elimination of infiltration of penumbra PMNsubsequent to initiation of stroke,the early brain injury does not influence the animal’s behavioral performance significantly[70].
It is not tough to appreciate regarding the significance of an inflammatory state being key for eliciting the neurotoxic potential of the invader.Resting state PMN illustrated no neurotoxic action in brain slices without Ischaemic prior damage along with just LPS stimulated PMN illustrated this action.An akin escalation of TREM1 takes place at the time of intestinal ischaemia reperfusion, however utilization of the hampering agent LP-17 postpones demise in experimental animals[71].The intestinal tract comprises of the major immune numerous organs possessing abundant or biggest immune cell pool that is implicated in 70% of the total immune system[72]. Intestinal microorganismson displacement can i) cause stimulation of intestinal associated lymphoid issue along with differentiation of immune cell subsetsii) facilitate the inflammatory reaction taking place in addition toiii) exacerbate the probability of systemic inflammatory reaction along with numerous organs impairment.
Microglia are obtained from the myeloid cellsof the yolk sac that have placement in the CNS early at the time of individual generation along with represent the resident immune cells of the CNS[73].The morphology of dendrites along with axons in case of neurons of germ free(GF) mice gets impacted at the time of generation as well as these kinds of generational abnormalities are usually correlated with immature microglial phenotype.This points to the key significance of gut microbial colonization at the time of generation of the brain[74]. Microglia possess the capacity of proliferation as well as polarization besides during a pathological situation from branching during resting state to an amoeboid state when activated [75].
Additionally, T lymphocytes possess a significant part in the stroke event.The Induction of dysbiosis duringacute phase of stroke facilitates proinflammatory Th1 along with Th17 modulated immune reaction obtained from peyers lymph nodes as well as aids in brain damage[57,76].On attainment of intestinal microecological homeostasis subsequent to during fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT),the quantities of Tregs escalate within the Ischaemic brain area[78].Chronic colitis in combination with stroke, migration of intestinal obtained CD4+Tcells takes place from intestines to the meninges along with might crosstalk with meningeal macrophages resulting in non-intestine obtained CD4+Tcells infiltration along with Tcells imbalanced M1 as well as M2 Microglia /macrophagesthat aggravates the brain damage in Ischaemic Stroke[79]. Simultaneously, it might further facilitate the migration of immune cells from the intestines to the damaged area of cerebral infarction as well as exaggerate the local damage.This might give us greater understanding regarding positive association amongst the intestinal barrier impairment as well as the extent of neurological sequelae in case of patients with cerebral infarction.Omit tissue
4.2Ectopic bacterial Placement subsequent to stroke result in infections of other tissues along with organs
Stroke can result in bacterial infections.A neurological central damage like stroke can cause a breakdown of the initial balance amongst the CNS in addition to the immune system, secondary immunodeficiency or immunosuppression.Finally this results in in the generation of infection[79].The ectopic bacteria that cause infection are exclusively species that are the ones part of intestinal flora which gain entry in the blood circulation followed by invasion of other tissues subsequent to stroke.An explanation offered for this is the escalated permeability of intestinal mucosa, colonization along with result in infections.Wen etal.[80], illustrated that there is aggravated impairment of the intestinal barrier with advancement of age facilitates translocation of gut obtained bacteria,aiding in escalated risk of post stroke bacterial infection.In an animal MCAO model,Tascilar etal.[81], observed that in post stroke Intestinal mucosa breakdown along with bacterial translocation inclusive of lung ,liver ,spleen along with mesenteric lymph nodes.The commonest pathogen is the coagulase negative Staphylococcus aureus .The dysfunctional intestinal barrier function generates a beneficial situation for Intestinal microbial translocation.
Nevertheless, Oyerna etal.[64], pointed to no significant variation in Intestinal mucosa alterations in animals at the time of acute phase of stroke: furthermore, their colonization in the lung might be associated with unintentional aspiration of the Intestinal flora into the trachea followed by in the lung at the time of gavage. Additionally,post stroke stress is further correlated with bacterial translocationfrom the colon into other tissue(like mesenteric lymph nodes, liver along with spleen) , escalates the inflammatory phenotype of the Intestinal mucosa(like COX2,iNOS) along with decreased the quantities of locally liberated IgA[82].This poststroke stress is correlated with stroke results[83].Irrespective of poststrokeinfection being the commonest complication, besides the maximum robust complication its mode required further evaluation.
5.Alterations of intestinal flora are intricately associated with poststroke depression
The brain -gut axis is a bidirectional controlling axis of the crosstalk amongst the brain as well as the Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). Gastrointestinal unease is usually correlated with emotional responses,that in turn can stimulate neural activities of the associated CNS regions. Simultaneously the controlling knowledge gets transferred to the GIT downwards via the brain -gut axis.This alters its dynamic besides the liberating functions, causes activation of Intestinal mucosal immunity along with impacting the Intestinal mucosal barrier function.Like in case of patients with gastroesophageal reflux,a robust association amongst anxiety, depression along with gastrointestinal symptoms like erosions of the gastric mucosa. Additionally,psychological or antidepressant therapy is efficacious for certain patients[84].In Psychiatric patients, depression along with generalized anxiety conditionsare usually correlated with gastrointestinal unease[85]. Numerous patients with generalized anxiety conditionsare usually initially diagnosed as having a gastroenterologic conditions [86]. Hence brain -gut axis impairment might participate in the formation of mental illnesses. Nevertheless, with regards to the mode,the present work suggests the implications of gut flora[87]. Alterations of BBB permeability takes place in the case of pathological condition [88] with different inflammatory factors gaining entry into the CNS.On transmission of inflammatory signals to the CNS, glial cell activation takes place via the NFκB pathway for facilitation of depression [89].
Post stroke depression gets frequently encountered in the post stroke population [90]. Patients in the post stroke phase in combination with cognitive dysfunction as well as depression usually possessed dysbiosis of the intestinal flora.PSCCID patients in contrast to non PSCCID patients, illustrated escalated enrichment of Proteobacteria, inclusive of,Gammaproteobacteria , Enterobacteriales along with Enterobacteriaceae besides reduction of Short chain fatty acids (SCFA) generating bacteria[91].
LPS delivery was observed to simulate depression like behavior in experimental animals. A remarkable inflammatory reaction in the CNS was seen that pointed that inflammatory reaction Induction by bacteria l with bacteria product like LPS possess the capacity of impacting CNS along with facilitation of depression generation [92]. Chronic mild stress results in escalated IL-1β, COX2 as well as PGE2 expressionin blood along with reduction inexpression of 15d PGE2 quantities in brain tissue. utilization of antibiotics could decrease inflammation through hampering TLR signaling pathway,hence this targetneeds evaluation regarding depression[93]. Hampering orblockade of TLRs implicated in CNS inflammation along with depression like behavior Induced by Chronic mild stress can result in recovery of inflammation along with behavior of the animal [94]. The Clinical manifestations of depression along with Chronic mild stress are akin to each other.The conclusionsdrawn from these present studies is that both share an akin pathogenesis. Nevertheless, recent studies have further demonstrated that the correlation amongst gut flora are not particular for Post stroke depression,advocating greater evaluation.Hence future experimental in addition to Clinical studies regardingthe assessment of actions of intestinal flora on Post stroke depression.
6.Modes possessing the capacity of conferring protection against Stroke via intestinal flora
The intestinal flora further possess the capacity of generating metabolites which promote improvement in stroke,out of which Short chain fatty acids (SCFA) is the one that has been maximum evaluated . SCFA represent one of the maximum frequent microbial metabolites obtained from the indigestible carbohydrate . SCFAs are comprised of acetate, butyrate, propionate in humans [95] besides lesser quantities of formate,valerate along with caproate[96].The absorption of SCFA into the circulation takes place actively with theuse of monocarboxylate transporters(MCTs) 97]. Furthermore, they possess the capacity of crossing blood brain Intestinal barrier (BBIB) [98]. In the Clinical studies it has been observed that lesser quantities of SCFAs have a robust association with Stroke along with stroke correlated Pneumonia (SAP) [99]. Fecal transplantation or SCFAs delivery cause enhanced stroke prognosis, of the lot butyric acid possesses maximum significance action, escalating the quantities of advantageous omits Lactobacilli along with reduction of intestinal mucosal permeability [100]. The assessment of intestinal microbiota in young along with elderly mice was conducted separately. Identification of greater quantities of SCFAs along with the strains which generate in the feces were seen in young mice. Bacteria forming SCFAs(Bifidobacterium longum,Clostridium symbiosum, Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii along with Lactobacillusfermentum) transplantation caused an escalated intestinal mucosal intactness, escalated SCFAs in blood along with brain tissue, Escalated Treg in brain tissue decreased IL-17+γδ T cells, decreased neuroinflammation, besides significantly enhanced behavior scores [101]As per Sadleret al.[102], multiple observations were noticeable i) reduction of quantities of SCFAs subsequent to strokeii)on artificial administration of SCFAs decreased the expression of CD68 in Iba-1+ along with caused reduction of microglia activation that decreased the inflammatoryreaction in the brain group subsequent to stroke. This in turn escalated synaptic plasticity in the semidark cortical zone, along with improvement of prognosis of stroke besides cortical reconstruction.This pointed that SCFAs generated by intestinal flora act in the form of basis of metabolites regarding the function of the gut brain axis .Besides complicated SCFAs, SCFAs species can work like butyrate by itself can confer neuroprotective actions.[103].
On liberation of bile in the intestine, metabolism of Bile Acid (BAs) into a pool of Bile Acids occur by the intestinal flora action. Subsequent to metabolism primary Bile Acids like cholic acid(CA), chenodeoxcholic acid(CDCA) Ursodeoxycholic acid(UDCA) are generated, followed by secondary Bile Acids like deoxycholic acid(DCA),lithocholic acid(LCA) get generated.These metabolites possess the capacity of binding different receptors in the brain,like Farsenoid Xreceptor(FXR)[104], TGR5(105), N-methyl-D aspartatereceptor (NMDAR)[106], along with PXR[107], following which biological action gets exerted.TauroUrsodeoxycholic acid(TUDCA)injection 1h subsequent to ischaemia escalated quantities of intracerebral BAs), decreased the size of infarction besides reducing neuronal apoptosis by escalating mitochondrial stability. Sustenance of this protective actions lasted for7d [108]. TUDCA possess the capacity of reduction of serum glutamate,TG,TC,LDL-C quantities, reduce the inflammatory factor expression, escalatedsuperoxidedismutase (SOD), catalase(CAT), glutathione peroxidase(GPx ) expression, decreased OS injury as well as downregulated nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor-2((Nrf2) signaling pathway in addition to proapoptotic protein quantities in cerebral ischaemic rats,hence confer neuroprotective actions[109]. Taking into account the broad kind of metabolites along with their continuous invention,the part of other species of BAs in Ischaemic Stroke requires further evaluation. Additionally, the Induction of neuroprotective actions of advantageous BAs species is feasible by manipulating intestinal flora.
Microorganisms that express tryptophanase in the intestine transform tryptophan to indoles,that on binding to aromatic hydrocarbons receptors facilitates the expression of β-catenin, Neurog 2 along with VEGF-α as well as facilitates neurogenesis in the hippocampus[110].This is remarkably in agreement with the observations of Mohle etal. [111], that observed that antibiotics therapy decreased hippocampal neurogenesis along with memory generation in adult mice, nevertheless, adoptive shift of Ly6C(hi) monocytes rescued this damage. SCFAs in physiological quantities possess the capacity of facilitating the growth rate of human neural progenitor cells(hNPCs), besides cause Induction of mitosis [112]. Facilitating neurogenesis or neural stem cells regeneration(figure3) can promote neurological recovery subsequent to stroke, hence intestinal flora might further escalate stroke results by facilitating the neural stem cells regeneration(figure3).
Courtesy ref no- 28 -Certain intestinal flora metabolites promote post-stroke recovery. Certain foods, such as high-fiber foods, can be metabolized by intestinal flora to produce SCFA, which is transported and absorbed by MCTs and enters the brain, reducing IL-17 + γδ T cells, diminishing activated microglia, and increasing synaptic plasticity; bile acids are transformed by intestinal bacteria into primary bile acids, which are then transformed into secondary bile acids and enter the blood or cross the blood–brain barrier, bind to receptors and upregulate SOD and GPX Tryptophan in food can be metabolized by enterobacteria to indole, which binds to intestinal mucosal aromatic hydrocarbon receptors and promotes the growth rate of human neural progenitor cells (hNPCs) by promoting β-catenin, Neurog2, and VEGF-α expression
7.Conclusions
Thus here we have summarized the alterations in gut microbiota(GM)that take placeduring IS.As we already know limited options of treating IS are available namely thrombolysis along with thrombectomy however a very short time window exists for same.Despite observing excitotoxicity, neuroinflammation along with oxidative stress(OS) working as the pathogenetic modes no clinical translation has been feasible.As earlier emphasized by us GM are implicated in the generation of unique immune abberations,metabolic abnormalities along with neurodegeneration(as reviewed by us earlier).Here we have further concentrated on the alterations in GM subsequent to ischemic stroke along with future utilization of this insight gained in treating IS besides getting biomarkers for prognosis
Additionally,as detailed earlier like age at initiation of stroke as well as gender[113-14],can further impact the results by influencing gut flora.MCAO, with the utilization of SD rats of separate genders documented that male SD rats displayed greater escalated intestinal mucosal permeability, greater escalated proinflammatory cytokines in the blood,having greater mortality in contrast to female SD rats[115]. In contrast to bacteria the part of fungi [116,117] in the gut has not been appropriately evaluated. Additionally,the name coined as the intestinal dark matter alias viruses[118]( inclusive of phages )are further presumed to possess greater significance in the disease despite lesser research has been conducted in this field.Thus factors that possess the capacity of alteration of intestinal flora require refinement followed by integration overall in the future studies planned.Basically every organism is indistinguishably correlated with each other instead of having independent existence with the presentation of microbiota -gut-brain axis in this particular fashion .Thus the evaluation on intestinal flora along with Ischaemic Stroke is presently in budding stage.We anticipate intestinal flora might become the newer target regarding nerve protection via multiple pathways in post stroke damage healing.Hence in future this intestinal flora targeting will have a significant part in primary as well as, secondary protection of Ischaemic Stroke[see figure4 &5 for details)[rev in ref 119].
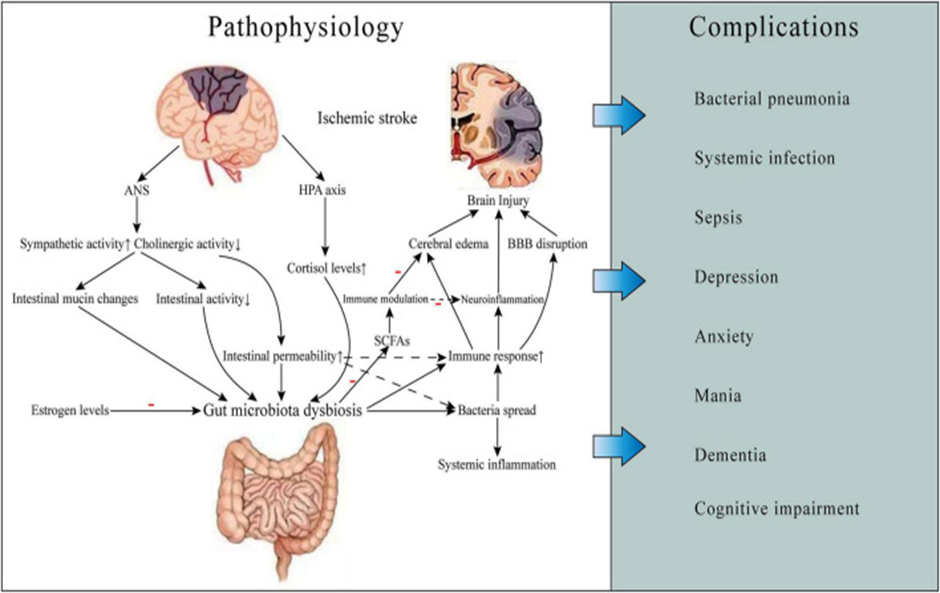
Legend for Figure 4
Courtesy ref no-119-Gut microbiota-related ischemic stroke pathophysiology and complications. Ischemic stroke can cause gut microbiota dysbiosis, which may result in increased gut permeability and worsening brain injury, thereby leading to some complications such as infections and neuropsychiatric disorders and poor prognosis. The mechanisms involved include neuroendocrine pathways, bacterial metabolite, and immune response. ANS, autonomic nervous system; HPA, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; BBB, blood-brain barrier; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids.
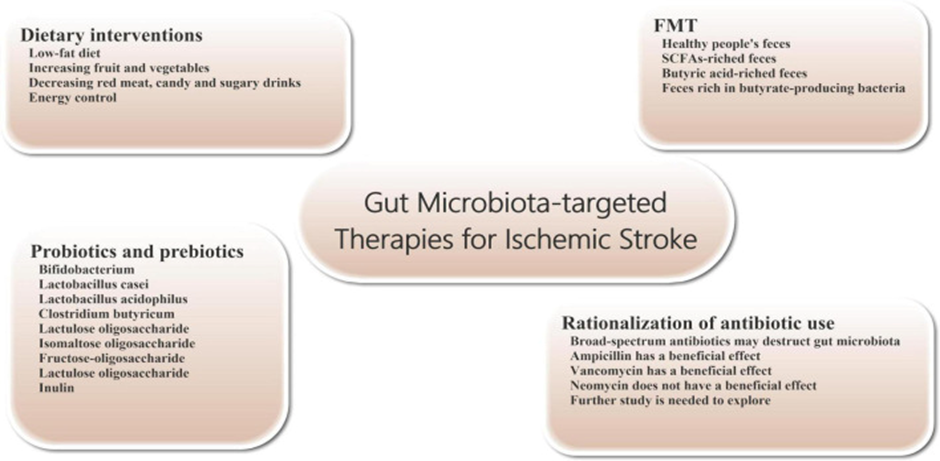
Legend for Figure 5
Courtesy ref no-119-Gut microbiota-targeted treatments and managements for ischemic stroke. Gut microbiota-targeted treatments and managements can be considered for patients with ischemic stroke, including dietary interventions, probiotics and prebiotics supplementation, FMT, and rationalization of antibiotic use. FMT, fecal microbiome transplantation.
References
- Tuttolomondo A.Ischaemic Stroke pathogenesis: genetics,epigenetics and inflammation.Curr Pharm Des 2020;26(34):4207-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - ZiaiWC,AlKawazM. Blood pressure management after endovascular therapy. Lancet Neurol 2021;20(4):248-9.
--> - Singh K,Chandra A,SperryT,JoshiPH,Khera A,Virani SS,etal. Association between High density lipoprotein particles and Ischaemic events by vascular domain,sex and ethnicity:a pooled cohort analysis. Circulation 2020;142(7):657-69.
Publisher | Google Scholor - SinghalS,BevanS,Barrick T,RichP,MarkusHS.The influenceof genetics and cardiovascular risk factorson the CADASIL phenotype. Brain 2004;127:2031-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - MohajeriMH,LaFataG,Steinert RE,WeberP.Relationship between the gut microbiome and brain function. Nat Rev 2018;76(7):481-96.
Publisher | Google Scholor - BreitbartM,HewstonL,Felts B,MahaffyJB,NultonJ,Salamon P,etal. Metagenomic analysis of an un cultured community from human feces.J Bacteriol 2003;185(20):6220-3.
Publisher | Google Scholor - NakaiH,Murosaki S,Yamamoto Y,Furutani M,MatsuokaR,HiroseY.Safety and efficacy of using heat killed Lactobacillus planetarium L-137high dose and long term effects on immunerelated Safety and intestinal bacterial flora.JImmunotoxicol 2021;18(1):127-35.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yang L,LuoH,Tan DC,Zhang SY,Zhong ZF, Wang SP,etal.A recent update on use of Chinese medicinein the treatment of inflammatory Bowel disease. Phytomedicine 2021;920(4):153709.
--> - Zhou Y, Zhang MH, Zhao X,F JH.Amnonia exposure induced Intestinal inflammation response injury mediated by Intestinal microbiota in Broiler chickens via TLR/TNF-alpha signaling pathway.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2021;226:12832.
Publisher | Google Scholor - KureckiC, Ozsoy B,HassanE,OzkanH,Gundogdu A,OzsoySYetal.Effect of essentialoil supplementation to diet on meat quality fatty acids, composition, performance parameters and Intestinal microbiota of Japanese quails.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 2021;105(5):927-37.
Publisher | Google Scholor - YangXQ,Yu DK,Xue L,Li H,DuJR.Probiotics modulate microbiota -gut-brain axis and improve memory deficits in aged SAMPB mice .Acta Pharmaceuticals Sinica B 2020;10(3):475-87.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Spychala MS,Venna VR,J M,Doran SJ,Durgan DJ,GaneshBP,etal.Age related changes in the gut microbiota influencesystemic inflammation and stroke outcomes. Ann Neurol 2018;84(1):23-36.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Brunetti V,Vollono C,TestaniE,Pilato F,DellaMG.Autonomic nervous system modificationsduring wakefulness and sleep in a case cohort of patients with Ischaemic Stroke.J Stroke Cerebrovascular Dis 2019;28(6):1455-62.
--> - NeedhamBD,Adams MD,SerenaG,Rose DR,Preston GM,Conrad MC,etal. Plasma and fecal metabolic profiles in autism spectrum disorder.Biol Psychiat 2021;89(5):451-62.
Publisher | Google Scholor - KarlJP,Margolis LM,Madslien EH,MurphyNE,Castellani JW,GundersenY,etal. Changes in the Intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased Intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am J Physiol Gastroenterol Liver Physiol 2017;312(6):G559- G571.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Li D,Ke YL,ZhanR,Liu CJ, Zhao MM,Zang AF,etal. Trimethylamine-N-oxide promotes brain ageing and cognitive impairment in mice. Ageing Cell 2018;17(4):e127368.
--> - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur,Allahbadia GN,Singh M. ’An update on the Generation of the Gastrointestinal Tract in Neonates with Specific Emphasis on the Hurdles Encountered in Feeding Preterm Infants with Associated Complications like Gut ,Brain &G-B Axis Generation:A Narrative Review’’.Under review 2022
--> - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur,Allahbadia GN,Singh M. The association of dietary fatty acids and gut microbiota alterations in the development of neuropsychiatric diseases: A systematic review. Obes Res Open J. 2020; 7(1): 19-45. doi: 10.17140/OROJ-7-143.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Clarke J,Grenham S,ScullyP,Fitxergald P,MoloneyRD,ShanahanF,etal.The microbiome gut brain axis during early life regulates hippocampal serotonergicsystem in a sex dependent manner.Mol Psychiatry 2013;18(6):666-73.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Angelucci F,Cechova K,AmlerovaJ,Hort J.Antibiotics, gut microbiota and Alzheimer’sdisease.JNeuroinflammation 2019;16:108.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Evenset A,Unselver BO,CeylanME.Psychobiotics. Front Psychiatry2019;1192:565- 81.
--> - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur,Allahbadia GN,Singh M. Weight Loss Associated with High Protein Diet Intake in Obesity: Interactions of Gut Microbiota in ProteinSources Influencing this Positive Effect”. Acta Scientific Nutritional Health2018; 2 (7): 80-89
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur,Allahbadia GN,Singh M. Intestinal Immune System in the Regulation of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome-Therapeutic Implications-A Systematic Review
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur .Delivered a talk on 30th September on ’Advantages and Limitations of utilizing Clostridium species as Probiotics-ASytematic Review’’ in a webinar held by Gastroenterology conference on 30th September 2021.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur,Allahbadia GN,Singh M. Have Probiotics and Synbiotics passed the test of time to be implemented in management of obesity and related metabolic disorders-a comprehensive review. Adv Obes Weight Manag Control. 2019;9(1):21‒28. DOI: 10.15406/aowmc.2019.09.00269
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur,Allahbadia GN,Singh M. Will Probiotics Provide the Answer for Therapy of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)? – A Systematic Review. Biochem Physiol 2020;9: 257.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kulvinder Kochar Kaur,Allahbadia GN,Singh M. ’Are we any close to unraveling the mechanism of interactions among susceptibility genes towards Type 1 Diabetes,Gut Microbiota Along with Environmental factors ,specifically early diet patterns –A Systematic Review’’
Publisher | Google Scholor - HuW,Kong X,WangH,LiY,LuoY. Ischaemic Stroke andIntestinal flora:am insight into brain-gut axis.Eur JMed Res 2022;27:73.
Publisher | Google Scholor - ChistiakovDA, Kashirskikh DA, Khotina VA,Grechko AV,OrekhovAN.Immunoinflammatory responses in Atherosclerosis:role of myeloid cells.J Clin Med 2019;8(11):1798.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hagakhia A, Li XMS, Liman TG,BledauN,SchmidtD,Zimmermann F,etal. Gut microbiota dependent Trimethylamine-N-oxide predicts risk of cardiovascular events in patients with Stroke and is related to proinflammatory monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2018;38(9):2225-35.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hayashi C,ViereckJ,Hua N,PhinikandouA,MadrigalA,Gibson FC,etal. Porphyromonas gingivalis accelerates inflammatory atherosclerosis in the innominate artery of ApoE deficienct mice. Atherosclerosis 2011;215(1):52-9.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Km VI,Bg I. induction of macrophage foam cells formationby Chlamydia Pneumoniae.J Infect Dis 1998;177(3):725-9.
Publisher | Google Scholor - VlacilAK,SchuettJ,RupertV,Soufi M,Oberoi R,Shahin K,etal. nucleotide binding oligomerization domains containing proteins 1 and2 reduces atherosclerosis.Basic Res Cardiol 2020;115(4):47.
--> - Brandsma F,KloosterhuisNJ,KlosterM,DekkerDC,Gijbels MJJ,VanDer Velden S,etal.A proinflammatory gut microbiota increases the risk of systemic inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis.Circ Res 2019;24(1):94- 100.
Publisher | Google Scholor - ChanYK,Brac MS,Kloosterhuis PV,Chen Y,Peng J,Li DX,etal. BMC Microbiol 2016;16:264.
Publisher | Google Scholor - DinAJ,HassanA, ZhuY,YinDY,GregersenH,WangGX.Amelioration of TMAO through probiotics and its potentialrole in atherosclerosis.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2019;103(23-24):9217-28.
Publisher | Google Scholor - FedotchevaN,OleninA,Beloborodova N. influence of microbial metabolites on the nonspecific permeability of mitochondrial membranes under conditionsof acidosis and Calcium and iron ions.Biomedicines 2021;9(5):558.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Tang WHW,WangZF,Levison BS,Koeth RA,BrittEB,Fu XM,etal. Intestinal microbial metabolism of phosphatidylcholine and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 2013;:368(7):1575-84.
Publisher | Google Scholor - YinJ,LiaoSX,He Y,Wang S,XiaGH,LiuFT,etal. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota with reduced Trimethylamine-N-oxide level in patients withlarge atherosclerotic stroke or transient ischaemic attack. J Am Heart Assoc 2015;4:e006885.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Zhu WF,RomanoKA,LiL,Buffa JA,Sangwan N,PrakashP,etal.Gut microbes impact stroke severity via the Trimethylamine-N-oxide pathway. Cell Host Microbes 2021;29(7):1199.
Publisher | Google Scholor - NemetI,SahaPP,GuptaN,Zhu WF,RomanoKA,Skye MA,etal.A cardiovascular diseaselinked microbialmetabolites act via adrenergic receptors.Cell 2020;180(5):862.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Xu X,LuWJ,ShiJY,SuYL,LiuYC,WangJ,etal.The gut microbialmetabolite phenylacetic glycineprotect against cardiac injury caused by ischaemia/ reperfusion through activating beta2AR.Arch Biochim Biophys 2021;697:108720.
Publisher | Google Scholor - HosomiN,AokiS,Matsuo K,DeguchiK,MesugataH,MuraoK,etal. Association of serum antiperiodontal pathogen antibody with Ischaemic Stroke. Cerebrovascular Dis 2012;34(5-6):385-92.
Publisher | Google Scholor - BenakisC,BreaD,Caballero S,FaracoG,MurphyJ,etal.Commensal microbiota affects Ischaemic Stroke outcome by regulating Intestinal gamma delta T cells. Nat Med 2016;22(5):515-23.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Sun J,Wang F,LIZX,YuXY,Chen WQ,LiHX,et al. Clostridium butyricum attenuates cerebral ischaemia/ reperfusion injuryin Diabetic mice via modulation of gut microbiota. Brain Res 2013;1642:180-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WuWF SunYF,LuoN,ChengC,Jiang CT,YuQP.etal.Integrated 16S rRNA gene sequencing and LC-MS analysis revealed the interaction between gut microbiota and plasmametabolites in rats with Ischaemic Stroke.J Mol Neurosci 2021;71(10):2095-106.
Publisher | Google Scholor - XuKY,GaoXX,XiaGH,ChenMX,Zeng NY,WangS,etal.Rapid gut dysbiosis induced by Strokeexacerbates brain infarction in turn . Gut 2021;70(8):1486-94.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WangHD,SongW,Wu QH,GaoXX,LiJ,TanCH,etal. Fecal transplantationfrom db/db mice treated with sodium butyrate attenuates Ischaemic Stroke injury. Microbiol Spectr 2021;9(2):e0004221.
Publisher | Google Scholor - JeonJ,LourencoJ,KaiserEE,WatersFS,ScheulinKM,FangX,etal. Dynamic changes in the gut microbiome at the acute phase of Ischaemic strokein a pig model. Front Neurosci 2020;14:58796.
--> - LeeS. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junctions: implications on inflammatory Bowel disease. Intest Res 2015; 13(1):11-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Takua S. Regulation of Intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci 2013;70(4):631-59.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Ye DY,HuY,ZhuN,GuWZ,Long G,TaoEF,etal.Exploratory investigations of Intestinal structure and function after Stroke in mice . Mediat Inflamm 2021; 2021:e1315797.
Publisher | Google Scholor - XiaZY,LuoC,LiuBW,BiaoXQ,LiY,PangAM,etal. ShenguiShansheng Pulvis maintains blood brain barrier Integrity by vasoactive Intestinal peptide after Ischaemic Stroke. Phytomedicine 2020;67:153158.
--> - WuJ,FanCJ,MaJ,LiuT,WangC,SongJX,etal. Distinctive expression signaturesof serum microRNAsin Ischaemic Stroke and transient ischaemic attack patients.ThrombHaemostat 2017;117(5):992-1001.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Nagata K,Sugi Y,Narabayashi H,KobayakawaT,NakanishiY,TsudaM,etal. Commensal microbiota induced Intestinal epithelial permeability the small GTPase-ARF4. JBiol Chem 2017;292(37):15426-33.
--> - Kurita N,Yamashiro K,Kuroki T,TanakaR,UrabeT,UenoY,etal.Metabolic endotoxaemia promotes neuroinflammation after focal cerebral ischaemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2020;40(12):2505-20.
Publisher | Google Scholor - SinghV,Roth S,Llovera G,SadlerR,GarzettiD,StecherB,etal. Microbiota dysbiosis control theneuroinflammatory response after Stroke. J Neurosci 2016;36(28):7428-40.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hyakkoku K,Hamanaka J,TsurumaK,Shimazawa M,Tanaka H,Uematsu S,etal. Toll like receptor 4 but not TLR3 or TLR9 knockout mice have neuroprotective effects against focal cerebral ischaemia. Neuroscience 2010;171(1):258-67.
Publisher | Google Scholor - RaJ,PjS,Giles B,M SE.Microbial disruption in the gut promotes cerebral endothelial dysfunction. Physiol Rep 2021;9(21):e15100.
Publisher | Google Scholor - YamashiroK,KuritaN,TanakaR,Kuroki T,UrabeT,HattoriN.Metabolic endotoxaemia promotes neuroinflammation after focal cerebral ischaemia.Int J Stroke 2020;15(1):612.
Publisher | Google Scholor - KawaiT,Akira S.The role of pattern recognition receptors in innate immunity:update on toll like receptors. Nat Immunol 2010;11(5):373-84.
Publisher | Google Scholor - GuoYJLi J,LiuM,LiCG, ChenYQ,Jiang C,etal. Impaired Intestinal barrier functionin a mouse model of hyperuricemia. Mol Med Rep 2019;20(4):3292-300.
Publisher | Google Scholor - JoshuaC,Rajkumar R,Rodney V,RVV,FudlongL,AnjaliC,etal. Ischaemic Stroke induces gut permeability and enhances bacterial translocation leading to sepsis in aged mice .Ageing 2016;8(5):1049-63.
Publisher | Google Scholor - OyernaN,Winek K,BackerKoduahP,ZhangT,DamesC,WenchM,etal. Exploratory investigations of Intestinal function and bacterial translocation after focal cerebral ischaemia in mice. Front Neurol 2018;9:937.
--> - VilaN,CastilloJ,DavalosA,CharnorroA. Proinflammatory cytokines and early neurological worsening of Ischaemic Stroke. Stroke 2000;31(10):2325-9.
Publisher | Google Scholor - AlMamunA,ChauhanA,Qi SH,NgwaC,XuY,ShameenR,etal. Microglial IRF5 IRF4 regulatoryaxis regulates neuroinflammation after cerebral ischaemia and impacts stroke outcomes. . Proc NatlAcad Sci USA 2020;117(3):1742-52.
Publisher | Google Scholor - BowmanCC,RasleyA,TranguchSL,MarriottL.C. Cultured astrocytes express toll like receptors for bacterial products. Glia 2003;43(3):281-91.
Publisher | Google Scholor - LiuQK,JohnsonFM,LamBK,WangQYeHB,WilsonEN,etal. peripheral TREM1 responses to brain and Intestinal immunogens amplfy Stroke severity. Nat Immunol 2019;20(8):1023.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Rubarelli A. DAMP mediated activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in brain Stroke:fine line between healing and neurodegeneration. Front Immunol 2014;5:1-2.
Publisher | Google Scholor - NeumannJ,RiekBuchardt M,Herz J,DoeppnerTR,Konig R,HuttenH,etal.Very late antigen-4(VLA-4) mediated invasion by neutrophils leads to interaction with microglia increased Ischaemic injury and impaired behavior in experimental Stroke.Acta Neuropathol 2015;129(2):259-77.
Publisher | Google Scholor - GibbotS.MausinE,AlauzetC,MonternnoniC,Lozniwiesky A,BozziartPE,etal. Effects of the TREM1 pathway modulation mesenteric during ischaemia reperfusion in rats. Crit Care Med 2008;36(2):504-10.
--> - ShiN,LiN,DuanXW,NiuHT.Interaction betweengut microbiome and mucosal immune system.Mil Med Res 2017;4:14.
--> - Alliot F,GodinJ,Pessac B. Microglia derive from progenitors originating from the yolk sac which proliferate in the brain.Dev Brain Res1999; 117(2):45-52.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Pronovost GN,Psiao EY. Perinatal interaction between the microbiome, immunity and neurodevelopment. Immunity 2019;50(1):18-36.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Ju FR,Ran YL,Zhu LR,ChengXF,Gao H,Xi XX etal. Increased BBB permeability enhances activation of Microglia and exacerbates loss of dendritic spines after transientglobal cerebral Ischaemia. Front Cell Neurosci 2018;12:236.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yu XB, ZhuoGY,Shao B, Zhuo H,XuCR,YanF,etal. -Gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by intracerebral haemorrhage aggravates in mice. Front Microbiol 2021; 12:647304.
Publisher | Google Scholor - SinghV,SadlerR,Heindl R,Llovera G,RothS, BenakisC,etal. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2018;38(8):1293-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Feng YK,He X, LuoSJ,ChenXF,LongSM,JiangFY,etal. Chronic colitis induces meningeal traffick of gut derived Tcells unbalance M1 and M2 Microglia /macrophages and increase brain injury in mice . Brain Res 2019;1707:8-17.
Publisher | Google Scholor - SchulteHerbaggenO,Quarcoo D, Meissl A,Meissl C.Differentialaffection of the Intestinal immune cellpopulation after cerebral Ischaemia in mice . NeuroimmunoModulation 2009;16(3):213-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WenSW,Shim R,Ho J,Wanrooy BJ,Srikhanta YN,KumarKP,etal.Advanced age promotes colonic dysfunction and gut derived lung infection after Stroke. Ageing Cell2019;18(5):e12980.
Publisher | Google Scholor - TascilarN,IrcorucoO, TascilarO,ComertF,Eroglu O,BahadirB,etal. bacterial translocation in experimental Stroke :what happens to the gut barrier.Bratisl Med J Bratisl Lek Listy2010;111(4):194-9.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Caso JR,Hurtado O,PereiraMP,GarciaBuenoB,MenchenL,Alou L,etal. Colonic bacterial translocation as a possible factor in stress worsening experimental stroke outcomes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2009;296(4):R979-85.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Caso JR,Pradillo JM,Hurtado O,LezaK,Moro M,LizasoainI. Toll like receptor 4 is involved in subacute stress - induced neuroinflammation in the worsening of experimental stroke Stroke 2008;39(4):1314-20.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Pooja B,Shahar B,Saameer K,Saameer K,Priyanka S, AhmadA,Panya D,etal. gastroesophageal reflux,disease in the young population and its correlation with anxiety and depression.Cureus 2021;13(21):e15289.
Publisher | Google Scholor - LiuPH,LiGZ, ZhangAX,YangCX, LiuZE,SunN,etal.Brain structural and functional alterations in MDD patients with gastrointestinal symptoms:a resting state MRI.J Affect Disord2020;273:95-105.
--> - Koloski N,Holtmann G,Tailey NJ.Is there a causal link psychological disorders and gastroenterologic disorders? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;14(11):1047-59.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Jiang WX,Gong L,LiuF,RenYK,MuJ. Alterations of gut microbiome and correlated lipidmetabolism in post stroke depression. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021;11:663967.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Stevens BR,Goel R, Seungbum,R,Richards EM,Holbert PC,PepineCJ,etal. increasedhuman Intestinalm barrier permeabilityplasma biomarkers zonulin and FABP2 correlated withplasma LPS and Altered gut microbiome in anxietyor depression.Gut 2018;67(8):1555.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yin OQ,Du T,YangCL,Li XL, ZhaoZY, LiuRT,etal.Gadd 45b is a novel mediator of depression like behavior and neuroinflammation after cerebral Ischaemia. Biochim Biophys Res Commun 2021;55:107-13.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Guo R,WangH,SunW,Liu FX.The advances in Post stroke depression. JNeurol 2021;30:1-4.
--> - Yi L,QiluG,Jumer Z,T JG,XionoengW,Jiameng L. structural changes in gut microbiotain patients with co-morbid cognitive impairment and its correlation with clinical features.J Alzheimer’sdisease 2021;77(4):1595-608.
--> - Cao P, Chen CM, ,Liu A,Shan OH, Zhu X,Jia CH,etal.Early life inflammation promotesdepressive symptoms in adolescent via microglialengulfment of dendrtic spines. Neuron 2021; 109(16):2573.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Garate I,GarciaBueno B,Madrigal EM,Bravo L,Berrocoso E,CasoIR,etal.Origin and consequences of brain toll like receptors 4 pathway stimulation of an experimental model of neuroinflammation of depression.J Neuroinflammation 2011; 8:1-4.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yan TX, WangNX, LiuB,Wu B,Xiao FS,He BS,etal. Shishandra chinensis ameliorates depression like behavior by by regulating microbiota -gut-brainaxis via the anti inflammationactivity.Phytother Res 2021;35(1):289-96.
Publisher | Google Scholor - CjH,PeW,BwJ,NcP,MgT. Short chain fatty acids in human largeIntestine,portal,hepatic and venous blood.Gut 1987;28(10):1221-7.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Macfarlane S, MacfarlaneGT. Regulation of Short chain fatty acids production. Proceedings of the Nutritional Society 2003; 62(1): 67-72.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Dalile B,VanOudenhoveL,Vervliet B,VerbekeK.The role of Short chain fatty acids in microbiota -gut-brain communication. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019; 16(8):461-78.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Claude B,Jean PierreC,Josef P. Short chain fatty acids in plasma andbrain: Quantitative determination by gas chromatography. Clin Chim Acta 1979;92(9):153-9.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Xia GH, Zhang MS,Wu QH,WangHD,ZhouHW,He Yetal. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota is an independent risk factor for stroke correlated Pneumonia:a Chinese pilot study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021;11:71545.
--> - ChenRZ, XuY, WuP, ZhouH,Lasanajak Y,Fang YYetal. Transplantation of Fecal microbiota rich in Short chain fatty acids and butyric acid treat cerebra Ischaemic Stroke by regulating gut microbiota. Pharmacol Res 2019;148:104403.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Lee J,D’Aigle J,Atadja J,Quaico V,Hodarpisheh R,Ganesh BP,etal. gut microbiota derived Short chain fatty acids promotes post stroke recoveryin aged mice.Circ Res 2020;12(4):453-65.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Sadler R,Cramer JV,HeindtS,Kostidis S,BetzD,ZuurbierKR, et al. Short chain fatty acidsimproves post stroke recovery via immunological mechanism .J Neurosci 2020; 40(5):1162-73.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Zhenhui Z,Ningbo X,Nathanael M,Wei MD,Yan D,Hui L,etal.Sodium butyrate attenuates neuronal apoptosis via GPR41/Gβγ/PI3K pathway after MCAO in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2020;67:267-81.
Publisher | Google Scholor - YanguanCasas N,Barreda MansoMA, Nieto SampedroM,Ramirez L.TUDCA an agonist of the Bile Acids receptor GPBAR1/TGR5with anti inflammatory immunological cells.J Cell Physiol 2017;232(8):2231- 45.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WangHB,ChenJ,HpllisterK,SowersLC,Forman BM. Endogenous Bile Acids areligands for the nuclear receptor FXR,BAR.Mol Cell 1999;3(5):543-53.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Koch A,BonusM,Gohlke H,KlockerN. Isoform Specific inhibition of N-methyl-D aspartate receptors by bile salts.Scientific Rep 2019;9:78.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Staudinger JL,GoodwinR,Jones SA,Hawlkin Brown D,Mackenzie KL,Latour A,etal.The nuclear receptor FXR is a lithocholic acid sensor that protects against liver toxicity. Proc NatlAcad Sci USA 2001;98(6):3369-74.
Publisher | Google Scholor - RodriquesTMP,Spellmann SR,Sola T,Grande AW,LinehanSteinC,Low TC,etal. Neuroprotection by a new Bile Acid in an acute stroke model of rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2002;22(4):461-71.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Buan KY,Jin HF, Sun W,SunYJ.DCAcan improve the ACI induced neurological impairment through negative regulation of Nrf2 signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019;23(1):343-51.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WeiGZ,MartinKA,Xing PY,Agrawal R,WileyL,Wood TK,etal. Tryptophan metabolizing gut microbes regulate adult neurogenesis via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. . Proc NatlAcad Sci USA 2021;118:27.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Mohle I.Mattei D,Heimmesaat MM,Berreswill S,Fischer A,Alutis M,etal. Ly6C(hi) monocytes provide a link between antibiotics induced changes in gut microbiota and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cell Rep 2016;15(9):1945-56.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yang H,Milischer V,Rodin S,Macfabe D,Villaescusa JC,Lavebrat C.Enteric Short chain fatty acids promote proliferation of human neural progenitor cells .J Neurochem 2020;154(6):635-46.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Wang QW,Qi YD,Shan WY,XuJLWang L,ChenSJ,etal.The aged Intestine performance and rejuvenation. Ageing Dis 2021;12(7):1693-712.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Miriam A, Mern DA, Bert HTT. A systematic review of the factors influencingmicrobial colonization of the preterm infant gut. Gut microbes.2021;13(1):31–3.
Publisher | Google Scholor - El-Hakim Y, Mani KK, Eldouh A, Pandey S, Grimaldo MT, Dabney A, et al.Sex differences in stroke outcome correspond to rapid and severechanges in gut permeability in adult Sprague-Dawley rats. Biol Sex Differences. 2021;12:1.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kexin D, Congmin W, Ping L, Yuan L, Xi M. Effects of Dietary Mycotoxinson Gut Microbiome. Protein Peptide Lett. 2017;24:5.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Eang HC, Wang OTP, Dei CP, Dang SP. Forgotten fungi-the gut mycobiomein human health and disease. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017;41:4.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Samtlebe M, Denis S, Chalancon S, Atamer Z, Wagner N, Neve H, et al.Bacteriophages as modulator for the human gut microbiota: Releasefrom dairy food systems and survival in a dynamic human gastrointestinalmodel. LWT. 2018;91:e45.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bao Z, Zhang Z, Zhou G, ZhangA,Shao A,ZhouF.Novel mechanisms and therapeutictargets for Ischaemic Stroke:Afocus on Gut microbiota. Front Cell Neurosci 2022;16:871720.
Publisher | Google Scholor
 Alcrut
Alcrut